Probate
We understand that dealing with probate can be a difficult and emotional experience. We know it’s hard to lose someone you love, and the probate process can be overwhelming. That’s why we are here – to help provide guidance and support during this challenging time. Our experienced team is dedicated to making the probate process as straightforward as possible so you can focus on your family and healing.
DeVries Law Firm, P.A.
WHAT IS PROBATE?
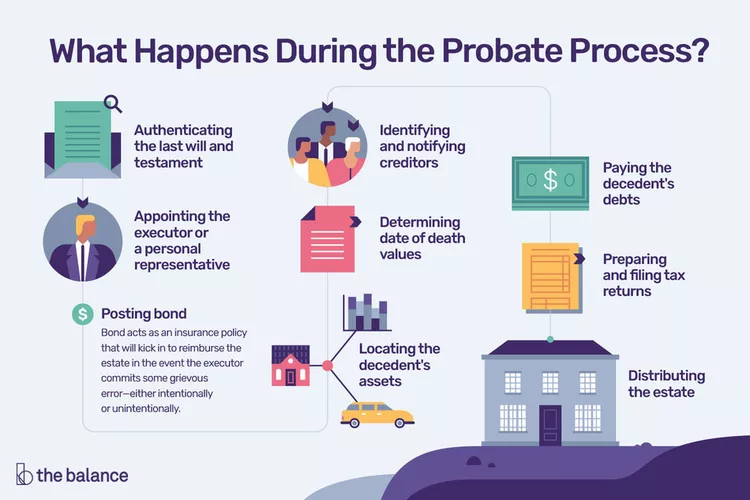
Probate is a legal process that occurs after someone passes away. It involves the management and distribution of a deceased person’s assets, including property, bank accounts, and personal possessions. In the United States, the probate process is regulated by state laws, and the court oversees the process to make sure that the deceased person’s property is distributed according to their wishes or, if they did not leave a will, to their heirs. Probate can be a complex and time-consuming process, involving various legal documents, court filings, and sometimes even litigation. Executors or administrators of the estate are responsible for handling the probate process, and it’s important to understand the steps involved to navigate the process smoothly.
Type of probate
Probate is a legal process where a person’s assets are distributed after their death. The executor files a petition to open the case and the court appoints a representative to manage the estate. The representative’s duties include finding, valuing, and paying debts. The remaining assets are then given to beneficiaries.
Summary administration
We Will Help You Every Step Of The Way
What People Say About Us
Client Testimonials
Frequently Asked Questions

The length of the probate process in Florida depends on several factors such as the complexity of the estate, the size of the estate, and any legal challenges or disputes that might arise. Generally, an uncontested probate case can take anywhere from six months to a year to complete. However, if the estate is large, complex, or involves complicated legal issues, the process may take several years to complete. Moreover, if there is an objection to the will or a dispute over the distribution of assets, the probate process can be significantly delayed.
Probate is the legal process by which a deceased person’s estate is distributed to beneficiaries according to their will or state laws. During probate, the executor of the will is appointed and must inventory all assets and notify creditors and heirs. Then, debts and taxes are paid from the estate before assets can be distributed to beneficiaries. If there is no will, the probate court will appoint an administrator and distribute assets according to state laws. The length of the probate process varies depending on the complexity of the estate, the state of residence, and any disputes among heirs or creditors. Probate can be a lengthy and costly process, but it is necessary to ensure that the deceased’s wishes are fulfilled and the property is distributed fairly.
Probate refers to the legal process that occurs after someone dies to settle their estate. It involves identifying and collecting the deceased person’s assets, paying any outstanding debts or taxes, and distributing the assets to the beneficiaries named in the will. Typically, assets subject to probate include real estate, vehicles, bank accounts, investment accounts, and personal property. However, some assets are exempt from probate, such as jointly-owned property with rights of survivorship, assets held in a trust, life insurance policies with named beneficiaries, and retirement accounts with designated beneficiaries. It’s important to note that the probate laws may vary depending on the state or country in which the deceased person resided, and seeking the advice of a qualified attorney or financial advisor may be beneficial.
Formal administration is the standard process for administering an estate in which a personal representative is appointed by a judge to handle all aspects of the estate, including paying debts, filing taxes, and distributing assets to beneficiaries. This process is typically necessary for estates that have significant assets and more complex legal issues.
On the other hand, summary administration is a simplified process that can be used for small estates with limited assets. This process involves the court overseeing the distribution of assets to beneficiaries without appointing a personal representative. The process typically involves filing a petition with the court, providing notice to creditors and beneficiaries, and filing a final report with the court.
In summary, formal administration is a more complex process that is used for larger estates, while summary administration is a simpler process that is used for smaller estates with fewer assets.
To initiate a probate case in Florida, the following documents are typically required:
1. Original copy of the deceased person’s will (if available).
2. Death certificate of the deceased person.
3. Petition for Administration form (this is a legal document that asks the court to appoint a personal representative to manage the affairs of the deceased person).
4. Oath of Personal Representative form (this is a legal document in which the personal representative swears to act in accordance with the law and duties of their appointment).
5. Notice of Administration form (this is a legal document that notifies interested parties, like beneficiaries and creditors, that a probate case has been initiated).
6. Inventory of the deceased’s assets (this is a list of all assets that belonged to the deceased person at the time of their death, such as bank accounts, investments, real estate, and personal property).
Note that depending on the specific circumstances of the case, additional forms or documents may be required.
Yes, there are alternatives to probate in Florida. One alternative is through the establishment of a revocable living trust. This allows assets to pass directly to beneficiaries without probate court involvement. Another option is for small estates under $75,000 to be settled through a simplified probate process called “Disposition without Administration”. Additionally, assets such as joint bank accounts or life insurance policies with designated beneficiaries can pass directly to the designated recipient upon the owner’s death without going through probate. Finally, there is a process called “Summary Administration” for estates with assets less than $1,000,000 that allows for a simplified probate process without the appointment of a personal representative. It’s important to consult with an attorney to determine which option is best for your individual circumstances.
In Florida, the process for distributing assets after probate involves several steps. First, the executor of the will (or administrator if there is no will) must find and secure all of the decedent’s assets. Then, they must pay off any debts or taxes owed by the estate. Once all debts are paid, any remaining assets will be distributed according to the decedent’s will or, if there is no will, according to Florida law.
The executor will need to file a final accounting and distribution with the court, which outlines all transactions made during the probate process. Once the court approves the final accounting and distribution, the executor can distribute the assets to the beneficiaries. The distribution may include transferring title or ownership of property, distributing cash or other assets, or making charitable donations, among other things.
The process can be lengthy and may take several months or longer to complete, especially if there are disputes or complex assets involved. It is recommended to seek the assistance of an experienced probate attorney to navigate the process.

If you have recently lost a loved one and are in need of probate assistance, we are here to offer you our support and guidance. Contact us today to schedule your free consultation and let us help you through this difficult time. We are committed to providing you with the support and assistance that you need to ensure that your loved one’s wishes are carried out in the way that they intended.
